Analysis Grid - Creating Charts and Gauges
Click the Add Chart tab or button to use the feature that lets you create charts and gauges. A separate Chart panel with its own configuration area will be displayed:
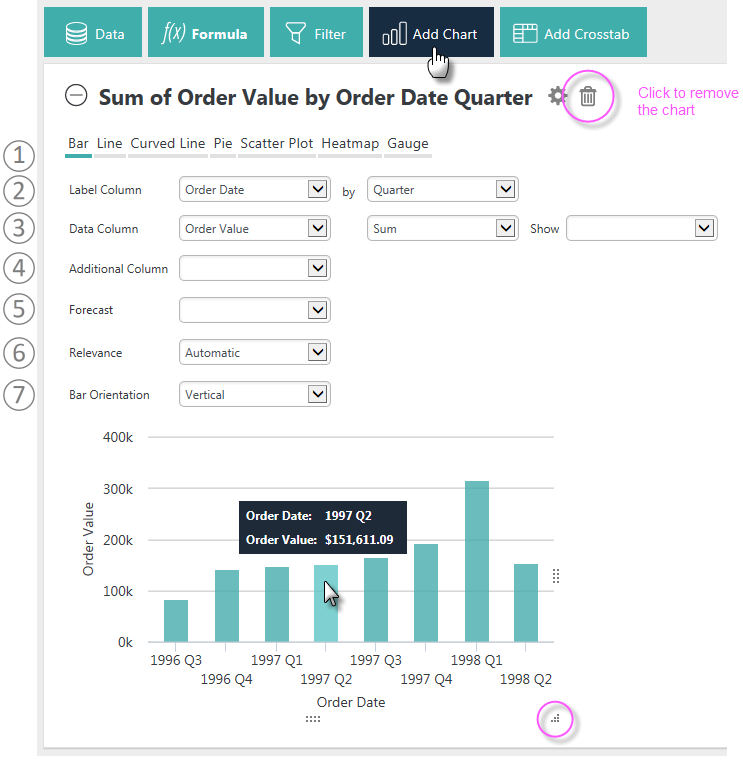
Here's how to use this feature (![]() some controls shown above only appear for specific data and chart types):
some controls shown above only appear for specific data and chart types):
- Click the option item for the type of chart to be created.
- Assuming a Bar chart was selected, select the Label Column. This provides data for the X-axis of the chart. If the column selected is a date-type column, an interval control (Year, Quarter, Month, Day, Hour, Minute) will be displayed.

For text type columns, you can select the Label data sort order, A-Z or Z-A, in a sort control. - Select the Data Column (Y-axis data, the "height" of each
bar). You'll see that the options are grouped and color-coded to make
it easier for you to identify them. If you created any Formula columns,
they'll be in there, too. You can also choose to show the actual data
values on the chart.
- Select a Data Aggregation function. Options include: Sum, Average, Standard Deviation, Count, Distinct Count, Minimum, and Maximum. Columns with Null values are excluded by default from aggregations.
- Select whether or not to show the actual data values as labels within the chart. - The Additional Column specifies a second data series that will be charted along with the Data Column values for comparison. Depending on the chart type, other controls will appear for use configuring a second series, including aggregation options and charting types.
- Data Forecasting is available for Bar, Line, Curved Line, and Scatter Plot (v12.2) charts. See the section below for more information.
- Relevance allows you to tune the data to be shown. Options include Automatic, Rank, and Percentage.
- Bar Orientation allows you to choose whether the bars are vertical or horizontal arrangements for Bar charts.
Depending on how your application is configured, you may see an "OK" or "Update" button that applies all of your selection changes to the chart at once. Otherwise, your chart will be redrawn immediately as you make individual changes.
Hide the chart configuration area by clicking the gear icon, or delete the chart completely by clicking its Remove (Trashcan) icon.
Charts are displayed in their own panels, so you can expand and collapse them using their "+" and "-" icons. You can also rearrange the order of chart and table panels by clicking with your mouse near the top of a panel, and dragging it up or down.
Charts will automatically include Quicktips, which appear when you hover your mouse over a data value, as shown above. In addition, "resizing handles" (circled above) will appear when the mouse is over the chart, allowing you to resize the chart by dragging them.
Unlike the chart shown above, Bar charts that are not time-oriented will
automatically be shown in a horizontal format. This
allows greater clarity in reading the "X-axis" label text.
Data Forecasting
Data Forecasting, if included by your application developer, is available for Bar, Line, Curved Line, and (in v12.2+) Scattercharts.
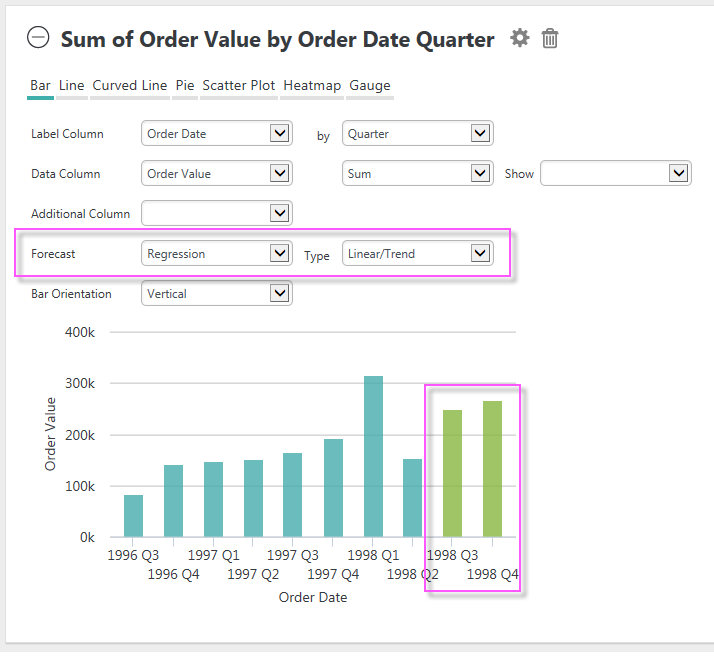
If it's available, extra controls for it will appear in the Chart configuration panel, as shown above.
Data forecasting is the process of generating values based on events that have not yet occurred. "Prediction" is a similar but more general term. Forecasting refers to formal, statistical methods that use time series, cross-sectional, or longitudinal data to produce predicted data. Typically, forecasts are displayed most effectively on charts.
Forecasting analysis options, which may vary by chart, include:
- Time Series (Time Series Decomposition), consisting of data in a natural, time-related order with a strong interval, where the Label Column data is of DateTime-type and the Data Column is a number.
- Regression, using one of several regression analysis functions. Regression
analysis is recommended when the focus is on a relationship between a
dependent value and one or more independent values. Available analysis functions include:
- Linear - used to calculate predictive values based on a trend line.
- Autoregressive
- used when attempting to predict an output of a system based on
previous outputs. The estimation technique used is based on "Burg's"
method.
- Exponential, Logarithmic, Polynomial, or Power - non-linear types
used to display the relationship between dependent and independent variables
as a curvilinear function, which may provide more accuracy than a
linear regression.