Format Classic Chart Label
Classic chart axis labels can be formatted using several special-purpose elements and, in addition to these, the actual label text of non-animated charts can be formatted using a language called CDML. This topic discusses CDML and its use.
- About CDML
- CDML Reference
- CDML Examples
About CDML
The static, classic charts in Logi product are created using components of the ChartDirector library. The ChartDirector Markup Language (CDML) can be used with the charts in order to format chart labels by marking them up with HTML-like tags. CDML allows a single text string in a Logi attribute value to be rendered using multiple fonts, on multiple lines, and with different colors.
For example, CDML can be used to add subscripted or superscripted characters to axis labels, such as "CO2" and "Km2", or to add a newline within a label, so it appears on two lines. Data used as labels can also be formatted. CDML provides powerful formatting features that can enhance your charts.
![]() Remember, CDML does not apply to Logi animated classic chart, map, or gauge elements, nor to Chart Canvas charts.
Remember, CDML does not apply to Logi animated classic chart, map, or gauge elements, nor to Chart Canvas charts.
CDML Reference
In general, all tags in CDML are enclosed by <* and *>. Attributes within these tags then determine the styles of the text following the tags, within the same block. If you want to include <* in text without being interpreted as CDML tags, use <<* as the escape sequence.
FONT STYLES
You can change the style of the label text by using CDML tags. For example, the line:
<*font=timesi.ttf,size=16,color=FF0000*>Hello <*font=arial.ttf,size=12,color=8000*>world!
in an chart's Label Title attribute will result in the following text being rendered:
![]()
The following table describes the supported font style attributes in CDML:
| CDML Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| font | Starts a new style section, and sets the font name. You may use this attribute without a value (that is, use "font" instead of "font=arial.ttf") to create a new style section without modifying the font name. Use <*/font*> to terminate a style section, which will restore the original font styles. |
| size | The font size. |
| width | The font width. This attribute is used to set the font width to different values. If the width and height are the same, use the size attribute. |
| height | The font height. This attribute is used to set the font height to different values. If the width and height are the same, use the size attribute. |
| color | The font color, in hex format, e.g. 000000. |
| bgColor | The font background color, in hex format, e.g. 000000. |
| underline | The line width of the line used to underline the following characters. Set to 0 to disable underline. |
sub | Sets the following text as subscript. |
super | Sets the following text as superscript. |
| xoffset | Draw the following the text by shifting the text horizontally from the original position by the specified offset in pixels. |
| yoffset | Draw the following the text by shifting the text vertically from the original position by the specified offset in pixels. |
Note that, unlike HTML tags, no double or single quotes are used within CDML tags. This is because CDML tags are often embedded as string literals in the parent page code and quotes, if used, may conflict with other string literal quotes. Therefore, quotes must not be used within CDML tags.
Also, unlike HTML tags, CDML tags use the comma character (,) as a delimiter between multiple tag attributes. This is because certain attributes, such as a font file name, may contain embedded spaces.
BLOCKS AND LINES
In CDML, a text string may contain multiple blocks. A block may contain multiple lines of text by separating them with the <*br*> tag.
For example, the line: <*size=15*><*block*><*color=FF*>BLOCK<*br*>ONE<*/*> and <block*><*color=FF00*>BLOCK<*br*>TWO</*>
in a chart's Label Title attribute will result in the following text being rendered:
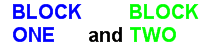
The example above uses a line of text that contains two blocks separated by the word and. Each block in turn contains two lines. The blocks are defined using <*block*> as the starting tag and <*/*> as the ending tag.
When a block ends, font styles will be restored to the state they were in before entering the block.
BLOCK ATTRIBUTES
CDML supports nested blocks; that is, a block can contain other sub-blocks. Attributes are supported within the <*block*> tag to control the alignment and orientation of the sub-blocks.
The following table describes the supported attributes inside a <*block*> tag:
| Block Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| angle | Rotate the contents of the block by this angle. The angle is specified in degrees of counter-clockwise rotation. |
| bgColor | The block background color, in hex format, e.g. 000000. |
| halign | The horizontal alignment of lines. This is for blocks that contain multiple lines. Supported values are left, center and right. The default value left means the left border of each line should align with the left border of the block. The value center means the horizontal center of each line should align with the horizontal center of the block. The value right means the right border of each line should align with the right border of the block. |
| height | The height of the block, in pixels. By default, the height is automatically determined to be the height necessary for the contents of the block. If the height attribute is specified, it will be used as the height of the block. |
| linespacing | The spacing between lines as a multiple of the default line spacing. For example, a line spacing of 2 means the line spacing is two times the default line spacing. The default line spacing is the line spacing as specified by the font used. |
| maxwidth | The maximum width of the block in pixels. If the content is wider than maximum width, it will be wrapped into multiple lines. |
| truncate | The maximum number of lines of the block. If the content requires more than the maximum number of lines, it will be truncated. In particular, if truncate is 1, the content will be truncated if it exceeds the maximum width (as specified by maxwidth or width) without wrapping. The last few characters at the truncation point will be replaced with "...". |
valign | The vertical alignment of sub-blocks. This is for blocks that contain sub-blocks. Supported values are baseline, top, middle, absmiddle, and bottom The value baseline means the baseline of sub-blocks should align with the baseline of the block. The baseline is the underline position of text. This is normal method of aligning text, and is the default in CDML. For blocks that are rotated, the baseline is the same as the bottom. The value top means the top line of sub-blocks should align with the top line of the block. The value bottom means the bottom line of sub-blocks should align with the bottom line of the block. The value middle means the middle line of sub-blocks should align with the middle line of the block. The middle line is the middle position between the top line and the baseline. The value absmiddle means the absolute middle line of sub-blocks should align with the absolute middle line of the block. The absolute middle line is the middle position between the top line and the bottom line. |
width | The width of the block in pixels. By default, the width is automatically determined to be the width necessary for the contents of the block. If the width attribute is specified, it will be used as the width of the block. If the width is insufficient for the contents, the contents will be wrapped into multiple lines. |
CDML Examples
Here are some examples of CDML in action in Logi applications:
CREATE A 2-LINE AXIS TITLE
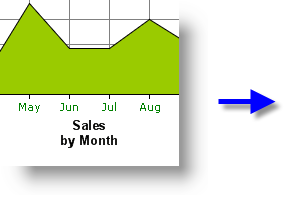
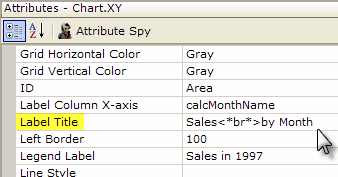
As shown above, a simple <*br*> tag is used in the Lablel Title attribute to produce a 2-line title.
USE SUBSCRIPTS IN AN AXIS TITLE
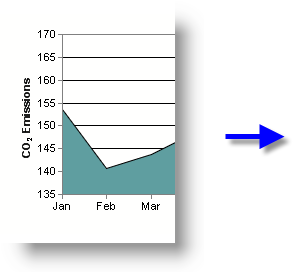
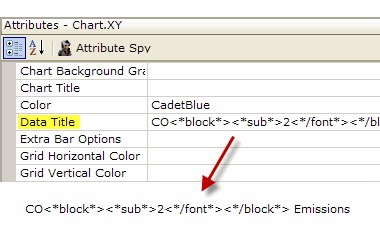
- As shown above, the <*block*> and <*/block*> tabs are used in the Data Title attribute to delimit the new font style.
- The <*sub*> tab specifies the new style (subscript).
- The <*/font*> tag ends the new style and returns to the original style.
USE SUBSCRIPTS IN AN AXIS TITLE


- As shown above, the <*block*> and <*/block*> tags are used in the Data Title attribute to delimit the new font style.
- The <*sub*> tag specifies the new style, i.e. subscript.
- The <*/font*> tag ends the new style and returns to the original style.
SET FONT SIZE AND ADD SUPERSCRIPT IN AN AXIS TITLE
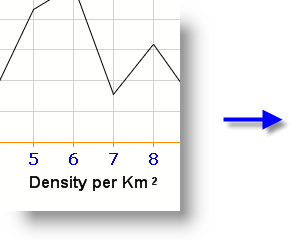
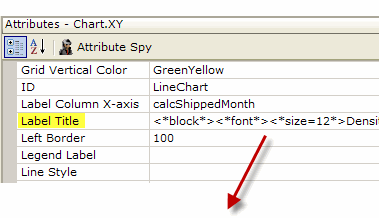
<*block*><*size=12*>Density per Km<*super*> 2<*/font*><*/block*>
- As shown above, the <*block*> and <*/block*> tags are used in the Label Title attribute to delimit the new font style.
- The <*size*> and <*super*> tags are to define the new font styles.
- The <*/font*> tag ends the new style and returns to the original style.
CREATE A 2-LINE DATA LABEL
To format data using CDML, it's necessary to first add a column to the datalayer to contain the formatted data.
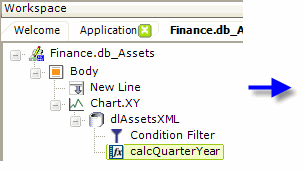
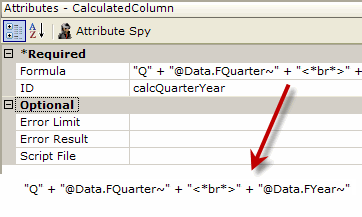
As shown above, a Calculated Column is used to combine the data from two coluimns and add a <*br*> tag in between them to put the data on two lines.
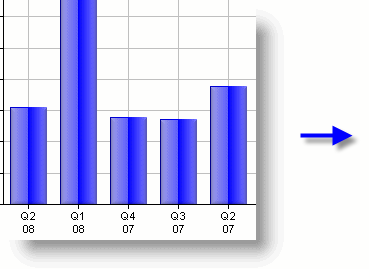
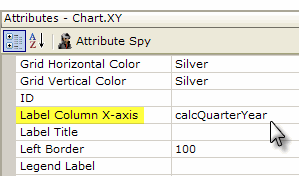
- The chart's Label Column X-axis attribute value is then set to the name of the calculated c olumn, as shown above.
Alternately, instead of using a Calculated Column element, the results shown in the example above could also be achieved by includingCDML right in the SQL query. For example:
SELECT FQuarter + '<*br*>' + RIGHT(FYear,2) AS calcQuarterYear FROM SomeSQLTable
would return a column that concatenated the values from two others with the CDML tag needed to insert the new line.