Conditions Example: Using the Division Element
A Division element is very useful as a container for other
elements and, through use of its Condition attribute, allows you to
selectively control whether it and its child elements, possibly entire
areas of application pages, are rendered.
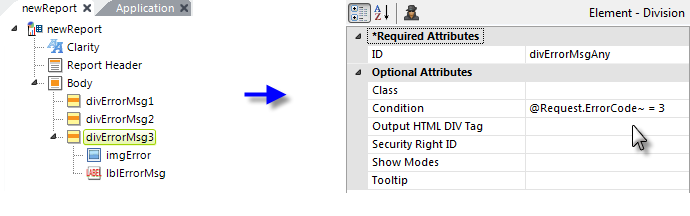
In the example shown above, three Division elements have been used to contain responses to specific potential errors.
If the Request variable and value ;"ErrorCode=3" is passed to this page when it's called, then the "divErrorMsg3" element will be displayed, along with its child elements, causing an error message to appear on the page. The other two Divisions, which have a similar expression in their Condition expressions but with a comparison to values 1 and 2, will not be displayed.
As mentioned earlier, the effect of displaying or hiding a Division element extends beyond just visibility; for example, datalayers within divisions will not run if the division is not displayed.
![]() Division elements include "HTML Attribute Params", enabling you to apply your application to work with other frameworks or libraries easier. With the HTML Attribute Params, you have the option to include "style" parameters:
Division elements include "HTML Attribute Params", enabling you to apply your application to work with other frameworks or libraries easier. With the HTML Attribute Params, you have the option to include "style" parameters:
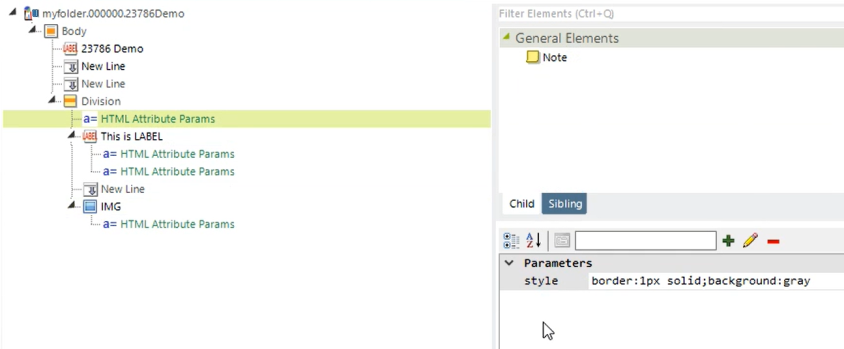
After the HTML Attribute Params are applied:
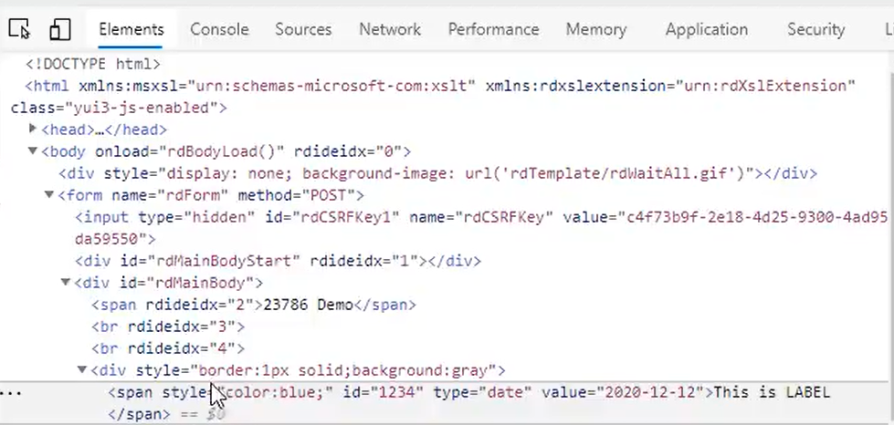
If an attribute was set in both Element and HTML attribute params, the one set in the HTML attribute params will be ignored.