Managing In-Memory Cubes
This topic shows you how to create, use, and manage in-memory cubes. In-memory cubes are cached data of business views. They are created by caching pre-computed aggregate functions called aggregations. Reports and visualizations use the cube data to improve performance. Fast in-memory analysis of data allows users to analyze and visualize data from any data source, including relational, cloud and big data sources.
The generating and updating of in-memory cubes are achieved by scheduling cube tasks. In-memory cubes are similar to scheduled reports that can be run immediately, run once at a specific time or run periodically to select the data from the DBMS and store it in Logi JReport Server. After an in-memory cube is created and ready for use, all reports, library components, and visual analyses that use the same business view as the in-memory cube will automatically use the cube rather than go to the database for the data. By applying in-memory cubes, your reporting performance will be greatly improved.
Below is a list of the sections covered in this topic:
- Creating In-Memory Cubes
- Viewing and Managing the Cube Tasks
- Recovering In-Memory Cubes
- Synchronizing In-Memory Cubes With Catalog Republish
Creating In-Memory Cubes
A business view can have only one in-memory cube. When a business view contains parameters, its in-memory cube can only represent the data of one parameter scenario.
Via Logi JReport's scheduling mechanism, administrators are able to define when an in-memory cube for a business view will be created and when it will be updated at a specific time or periodically. This is especially useful for month and quarter end reports where multiple reports use the same dataset with the same parameters such as begin and end date.
In-memory cubes have no versions: once they are updated, only the latest one is kept for the business view.
To create an in-memory cube:
- In the Logi JReport Server console, point to Administration on the system toolbar, and then select Configuration > Cache > Cube from the drop-down menu to display the Cube page.
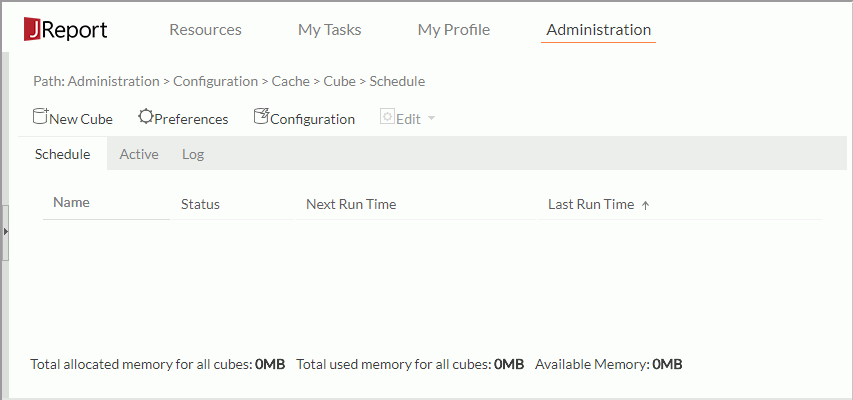
Note: If it is the first time to create in-memory cubes, the administrator needs to first configure the maximum memory allowed for all in-memory cubes. To do this, select Configuration on the task bar of the Cube page (this option is not available to organization admins), then in the Maximum Cube Memory Allowed text box specify the allowed maximum cube memory size in megabytes. The total allocated memory for each cube cannot exceed this value. It does not take into consideration the actual memory used by the in-memory or if some of the cubes are swapped to disk. This value should not be larger than 80% of your Java Heap size.
- Select New Cube on the task bar. The New Cube dialog appears.
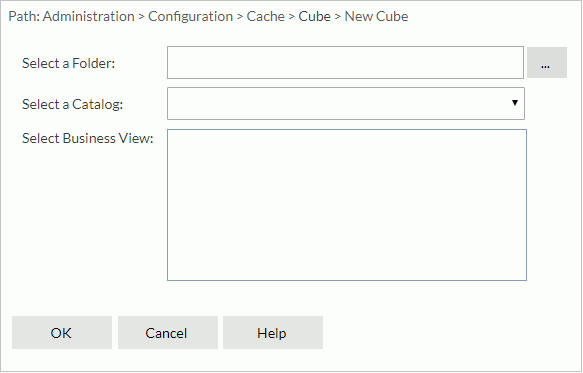
- Select
 next to the Select a Folder text box. In the Select Folder dialog, browse to the folder containing the required catalog and select OK.
next to the Select a Folder text box. In the Select Folder dialog, browse to the folder containing the required catalog and select OK. - From the Select a Catalog drop-down list, select the required catalog in the specified folder.
- In the Select Business View box, select the business view on which to create the in-memory cube. The business view name will be used as the name of the in-memory cube.
- Select OK to confirm the selection. The tabs for defining the schedule task information are then displayed.
- In the General tab,
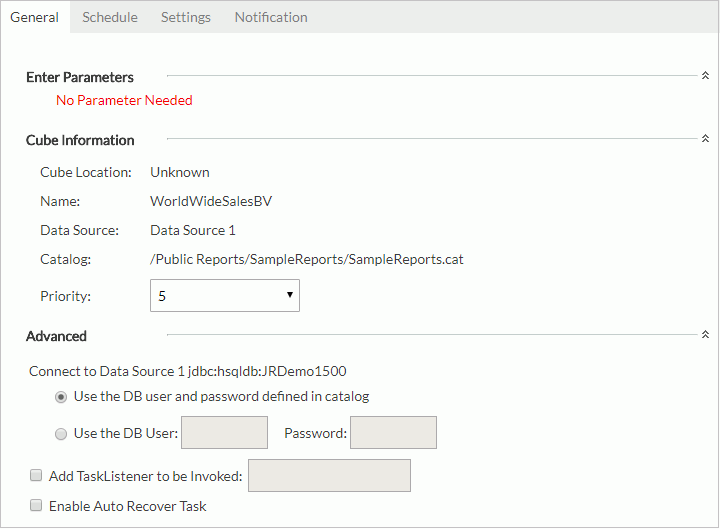
- Specify the parameter values if the business view uses parameters.
- Expand the Cube Information section, assign a priority to the task from the Priority drop-down list. The priority levels are from 1 to 10 in ascending order of lowest priority to highest priority (by default this property is ignored unless server.properties is modified to set queue.policy not equal to 0).
- Expand the Advanced section to configure some advanced settings.
Specify the DB user and password with which to connect to the data source. You can either use the default ones defined in the catalog or specify another DB user and password.
Check the Add TaskListener to be Invoked option to call a Java application before/after the task runs so as to obtain information about the task (for details, see Applying TaskListener).
If you are in a cluster environment, you can also directly specify an active server in the cluster to perform the schedule task via the Specify a preferred server to run the task option.
If you want to enable task recovery, check Enable Auto Recover Task, then specify the maximum number of times in which to retry running the task in order to recover it, the time interval between the retries, and whether to recreate all or just the failed results.
- In the Schedule tab, specify the updating policy of the in-memory cube.
- In the Time sub tab, specify the time zone and the time for when the task is to be performed.
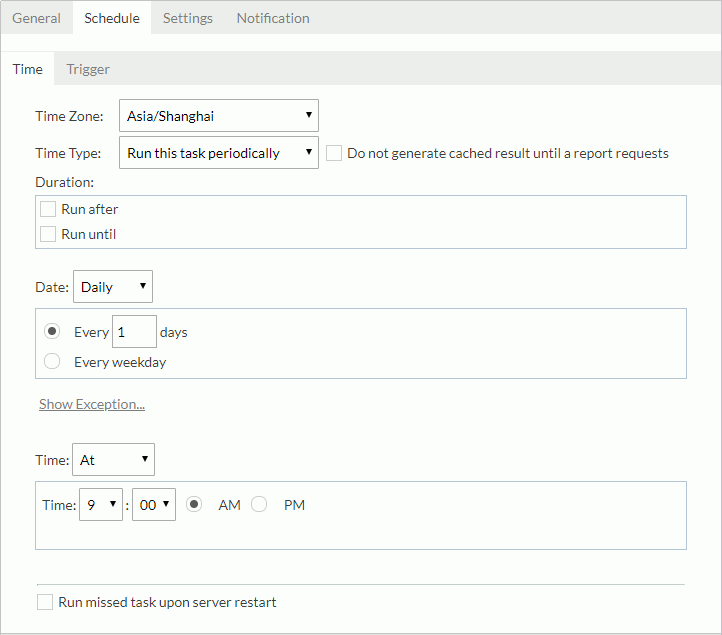
- To run the task as soon as you submit it, select Run this task immediately from the Time Type drop-down list.
- To run the task at a specified time, select Run this task at, then define the time according to your requirement.
- If you want to run the task repeatedly, select Run this task periodically, then specify the duration, date and time accordingly. By default, the task will be performed according to the specified time condition to generate the in-memory cube. If you prefer to run the task only upon the first report running request based on the business view after each scheduled time, check Do not generate cached result until a report requests. To add an exception date on which you do not want to run the task, select Show Exception, then select the Add button and in the Select Condition dialog select the date as required. You can add several exception dates as you want. To remove an exception date, check it in the exception date box and select Remove.
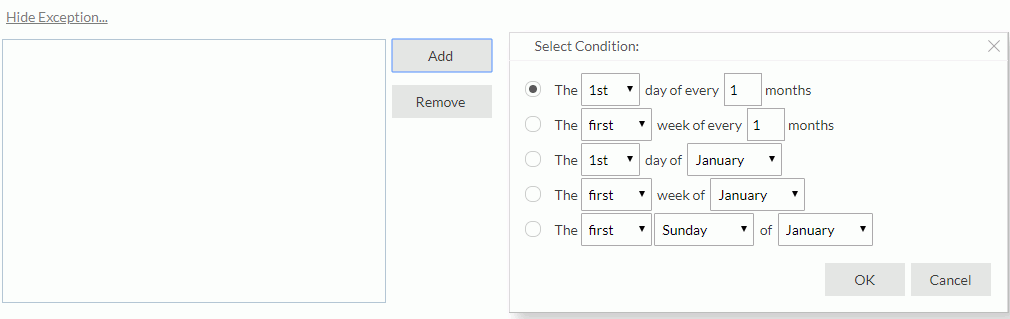 .
.
When you select to run the task at a specified time or repeatedly, check Run missed task upon server restart so as to run the missed tasks when you restart the server if needed.
- If you want to bind a trigger to the task, switch to the Trigger sub tab.
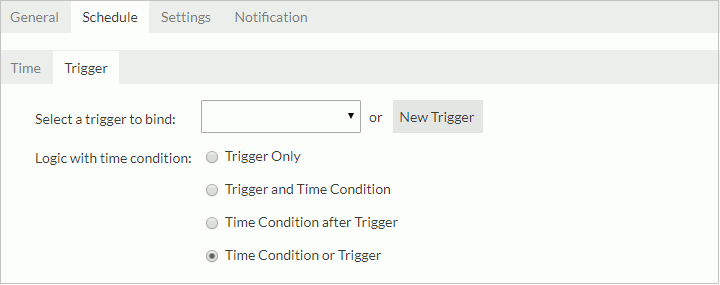
From the Select a trigger to bind drop-down list, select the required trigger or select the New Trigger button to create a new trigger in the New Trigger dialog (the button is not available to organization admins), then specify the trigger logic with time condition.
- Trigger Only
Performs the task only when the trigger is fired. - Trigger and Time Condition
Performs the task when both time is up and the trigger is fired.Note: When this logic is selected:
- No matter which condition is ready, the task can only be performed when its counterpart is ready.
- If you specify the task to be performed at a specific time, you must check the option Run missed task upon server restart, otherwise the task will be regarded as expired and will be deleted when the time condition is ready before the trigger condition.
- Time Condition after Trigger
Performs a task when time is up after the trigger is fired. If the time condition is ready before the trigger condition, the task will be regarded as expired and will be deleted. - Time Condition or Trigger
Performs the task when either time is up or the trigger is fired.
- Trigger Only
- In the Time sub tab, specify the time zone and the time for when the task is to be performed.
- In the Settings tab,
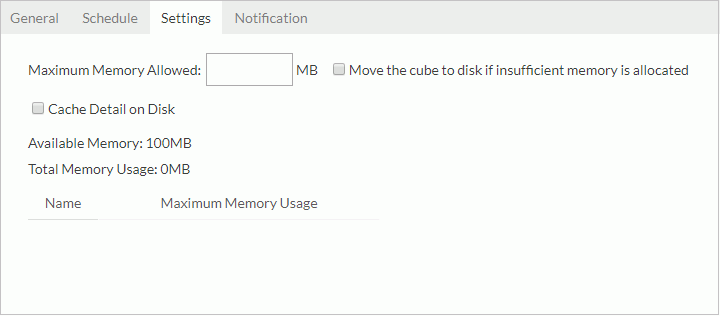
- In the Maximum Memory Allowed text box, provide a value for the cube. The value must be specified, otherwise you are not allowed to continue with other tabs or to finish the dialog.
- If you would like to cache the cube on disk once the available memory is exhausted, select Move the cube to disk if insufficient memory is allocated. If this option is not selected and the memory is not enough for the cube, the cube status will be disabled and an error will be shown in the log tab.
- If you would like the detail data in the business view to be cached onto disk, select Cache Detail on Disk. Otherwise if you need only the aggregation data to be cached, unselect the option.
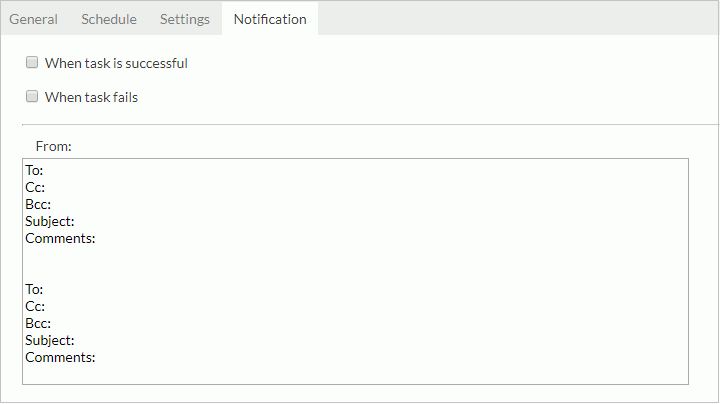
- In the Notification tab, specify to notify someone via e-mail of when the task is finished successfully or when it fails, then in the mail box, enter the information of the receivers and the mail content. To send out mail notification, an e-mail server must have been predefined by the administrator.
- Select Finish, and Logi JReport Server will then perform the task at the requested times.
After an in-memory cube is created and ready for use, all reports, library components and visual analyses based on the same business view as the cube will automatically use the cube for retrieving data.
Since an in-memory cube freezes parameters in its related business view, if a report uses an in-memory cube and its business view contains parameters, when running the report, only parameters used in the report are available for specifying values and the business view parameters will be disabled for editing. In Logi JReport, a parameter may depend on another parameter; if the latter is frozen, the former will be frozen as well.
Viewing and Managing the Cube Tasks
You can view information of the tasks scheduled for creating in-memory cubes and manage the tasks in the Schedule, Active, and Log tables in the Cube page.
All scheduled cube tasks are listed in the Schedule table. You can edit any of the tasks in the table in the following ways:
- To further edit the scheduling information of a task, select the row in which the task is located, then select Edit > Properties on the task bar, or the Properties button
 on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the row and select Properties on the shortcut menu. In the displayed dialog, edit the scheduling information. If parameters or schedule policy is changed, they will only take effect after the next cube update; before that, all reports using the cube will still get the old data.
on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the row and select Properties on the shortcut menu. In the displayed dialog, edit the scheduling information. If parameters or schedule policy is changed, they will only take effect after the next cube update; before that, all reports using the cube will still get the old data. - To disable a task that is not disabled, select the row where the cube task is, then select Edit > Disable on the task bar, or the Disablebutton
 on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the row and select Disable on the shortcut menu.
on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the row and select Disable on the shortcut menu. - To enable a task that is disabled, select the row where the cube task is, then select Edit > Enable on the task bar, or the Enablebutton
 on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the row and select Enable on the shortcut menu.
on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the row and select Enable on the shortcut menu. - To remove a task that is no longer required, select the row where the cube task is, then select Edit > Delete on the task bar, or the Deletebutton
 on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the row and select Delete on the shortcut menu.
on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the row and select Delete on the shortcut menu.
The following lists the columns in the table:
All the cube tasks that have generated in-memory cubes which have data and are ready for use are listed in the Active table. You can edit the tasks here in the same way as you do in the Schedule table.
The following lists the columns in the table:
| Column | Description | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | The name of the cube task. | ||||||||||||
| Catalog | The catalog that the cube belongs to. | ||||||||||||
| Data Source | The data source that the cube belongs to. | ||||||||||||
| Updated Time | The last time when the cube was updated. | ||||||||||||
| Allocated | The maximum memory allowed for the cube. | ||||||||||||
| Actual | The memory size currently used by the cube. | ||||||||||||
| Located At | Shows the location of the cube:
| ||||||||||||
| Parameter | Displays a parameter icon. By selecting the icon a dialog will appear to show all the parameters used in the cube. | ||||||||||||
| Usage | The number of reports and library components that have accessed the cube. If the number is bigger than 0, select it and you will get a detail table showing the information of all the web reports and library components that used data from the cube.
The detail table contains the following columns:
|
All the events happened on all the cube tasks are recorded in the Log table. You can delete any of the log records from the table if you want. To do this, select a record row and then select Edit > Delete on the task bar, or the Deletebutton  on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the record row and select Delete on the shortcut menu.
on the floating toolbar, or right-click on the record row and select Delete on the shortcut menu.
The following lists the columns in the table:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the cube task. |
| Catalog | The catalog that the cube belongs to. |
| Data Source | The data source that the cube belongs to. |
| Activities | The type of the event:
|
| Start Time | The time when the event started. |
| End Time | The time when the event ended. |
| Status | The event status: Successful or Failed. |
| Message | Messages for failed events. |
Tips:
- You can customize the columns shown in the tables as follows: switch to the table, select Preferences on the task bar of the Cube page, check the corresponding items in the Preferences dialog, then select OK to apply the settings.
- You can make the records in each table sorted ascending or descending by any column title. To do this, select on the underlined column title on which you want the records to be sorted, you will then find a sort icon appear right after the title, showing the sort direction.
Recovering In-Memory Cubes
If an in-memory cube is updating when the server shuts down, the cube will be disabled after the server restarts. Administrators need to enable the cube task in order for the cube to continue to update at the next scheduled time.
Synchronizing In-Memory Cubes With Catalog Republish
After a catalog is republished, how the existing in-memory cubes based on the old business views in the catalog will be updated depends on the following conditions:
If no business view is modified, the existing in-memory cubes will be automatically applicable to the new catalog.
If a business view is modified, the in-memory cube based on the old business view will behave as follows:
- Before the next schedule time, the cube will be disabled for retrieving data to reports.
- When it is the next schedule time, data is fetched from the new business view to generate an updated cube:
- If new parameters are added in the new business view, default values will be used until an administrator specifies values to them.
- If old parameters are deleted from the new business view, the parameter values previously specified in the cube will be removed.
- If parameters are changed and the previously specified values do not match the type, error messages will be given in the server error log and the cube is disabled for service.
 Previous Topic
Previous Topic