Dynamically Filtering Queries
You can use a parameter in a WHERE clause so that the query result can vary each time according to the entered parameter value. This works the same for Logi JReport queries created with the Query Editor, imported SQL files, business views and datasets. When using imported SQL, simply put @ParamterName or :ParameterName directly into the SQL file to be imported. Logi JReport will provide the default values when you import the file so the database recognizes the syntax. This is the most common usage of parameters. See the following example.
- Open the catalog file SampleReports.cat in
<install_root>\Demo\Reports\SampleReports. - In the Catalog Manager, expand the desired data source and create a type-in parameter named IDSet of Integer type with the default values 1, 10, and 20, and enable the Allow Multiple Values option.
- In the same data source, create a query CustomersInfo on the table Customers. Select all the fields contained in the table.
- In the Query Editor, select Menu > Query > Filter.
- Filter the records of the query by adding a condition as follows in the Search Condition dialog (for details, see Filtering with the Filter Format):
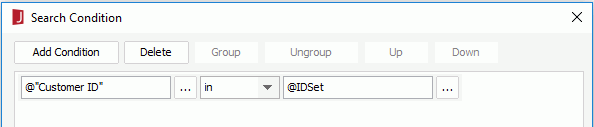
- Create a page report with a table in it based on the query as follows: have the fields Customer ID, Customer Name, City and Phone displayed in the table and apply the Commercial style.
- View the report. In the Enter Parameter Values dialog, select
 next to the value field of IDSet.
next to the value field of IDSet. - In the Enter Values dialog, uncheck the All option, add the listed values 1, 10, and 20 to the right box, and then select OK. You will find that the records with Customer ID equal to 1, 10 and 20 have been retrieved.

- View the report again. This time, in the Enter Values dialog, remove 1, 10, and 20 from the Selected Values box first. Enter the values 3, 7, 9, 11, 15, and 25 in the Enter Values field and add them into the Selected Values box one by one. Then select OK. Now, the records for the specified Customer IDs are displayed.

To view the report with full data, select the All option and then select OK in the Enter Values dialog.
Notes:
- The parameter's data type must be set according to the field type and the manner in which you use the parameter. For example, if the field is a number, define a parameter to be Number type also.
- If you set the parameter format to be @ParameterName, to specify a String type value, your typed value should be without single quotations, for example, USA. Once you input a parameter value with single quotation marks, the quotation marks will be recognized as a part of the parameter value.
However for the format :ParameterName, to specify a String type value, your typed value should be with single quotations, for example, 'USA'. If the data type is Number, the parameter value should be without quotes in both cases: 1234.
 Previous Topic
Previous Topic