DataLayer.Excel
Developers often need to read data from Microsoft Excel spreadsheets. Prior to the 9.1 release of Logi products, an OLEDB connection and the Microsoft Jet or Access driver was used to access this data. Now developers can instead use a datalayer element dedicated to the task, DataLayer.Excel. This topic discusses this new datalayer.
- Attributes
- Working with DataLayer.Excel
Attributes
The DataLayer.Excel element has the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Excel File | (Required) Specifies the fully-qualified file system path and filename for the spreadsheet file. The token @Function.AppPhysicalPath~ can be used to get the application folder path. Both .xls and .xlsx formats are supported. Example: @Function.AppPhysicalPath~\SampleData\Contacts.xls A fully-qualified URL to an Excel file on the Internet can be specified instead, such as: http://www.example.com/data/records.xls |
| ID | (Required through v10.1.46) The unique element name. |
| Cell Range | Specifies a range of cells from the worksheet to be read. Multiple ranges, separated by commas, can be specified and will be joined together to include all matching columns and rows. Examples: A1:H10 will include rows 1 through 10 of columns A through H. |
| Column Names | If left blank and if the Column Names Row attribute has no value, columns retrieved into the datalayer will be assigned default names in the form: Column1, Column2, Column3, etc. If, however, an optional comma-separated list of custom datalayer column names is specified here, they will override the default names. Or, if the Column Names Row attribute specifies a row number, valid text names from the specified data row will automatically be assigned as the datalayer column names, overriding the default names. |
Column Names Row | Specifies the row number which contains names for the datalayer columns. This row will not be included in the data, but will be used as column names when the data is valid (names should start with a letter and include only letters or numbers). |
| Date Columns | Specifies a comma-separated list of column names of those columns that should be formatted as DateTime data. The names entered here should match those specified using earlier attributes for the datalayercolumnnames, e.g. these may be the default names: Column1, Column5, etc. or the custom names specified in the Column Names attribute, or the names read from the row specified in the Column Names Row attribute. |
| Worksheet | Specifies the worksheet in the Excel file from which to read data. The default value is the first worksheet. |
Working with DataLayer.Excel
In most respects, DataLayer.Excel functions exactly as other datalayer elements do and its data can be filtered and conditioned using appropriate elements. One major difference, however, is that there is no need to use a Connection element in the _settings definition with this element. The DataLayer.Excel element directly accesses the file system to read .XLS and .XLSX files.
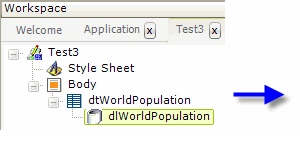
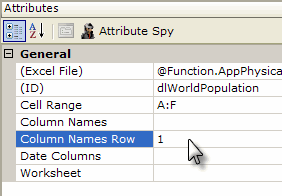
As shown above, a DataLayer.Excel element is added as a child element to a data table or other data container element. Its attributes are set so that it accesses the desired Excel file, reads the right worksheet and columns, and so it handles column names as desired.
The datalayer reads and caches the data from the Excel file. You can add child elements beneath the datalayer to affect its contents, including:
- Filtering: Sort, group, or restrict the data
- Extending: Add virtual columns to the datalayer that contain aggregated, calculated, or totaled data values
- Securing: Limit access to the data using Logi security
- Linking: Make the results reusable elsewhere in your report definitions
The use of many of these elements is described in separate DevNet documents.
Data read into the datalayer is cached in XML format in memory and/or on the web server's file system. The latter is discussed in The Logi Server Engine and may be of interest to developers working with extremely large datasets or large numbers of concurrent users.
The data read with the datalayer is available using @Datatokens, in the format @Data.ColumnName~. The spelling of the column name is case-sensitive. The data is only available within the scope of the parent element of the datalayer, not throughout the entire report definition. The DataLayer.Linked element can be used to make the data reusable in another datalayer outside this scope.
In Logi Info, the Auto Columns element can be used to quickly display in your report all the data in a datalayer.
The data retrieved into the datalayer can be viewed by turning on the
Debugging Link in your _settings definition (General element) and using
the resulting link at the bottom of your report page to view the Application
Trace page. A link on the Trace page will display the retrieved data.
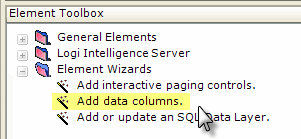
Studio includes a wizard that will add elements for the columns in the datalayer to your definition. You can select the desired columns before the operation begins. With the datalayer's parent Data Table or similar element selected in the Definition Editor, click the wizard link, shown above, in the Element Toolbox.