The Contain Filter
The Contain Filter element is used with datalayer elements to filter out data rows. It's analogous to using a WHEREx CONTAINS y clause in a SQL query but, unlike a query, it's applied to the data after it's been retrieved into the datalayer. This topic discusses use of this element.
- About the Contain Filter
- Apply the Contain Filter
- Use Multiple and Dynamic Contain Filters
This element is not available in Logi Report.
About the Contain Filter
The Contain Filter element, introduced in v10.1.18, is available for use with all datalayer elements and is particularly useful in conjunction with those lacking query capabilities, such as DataLayer.XML and DataLayer.Web Service.
In operation, the element basically searches a specified data column value for a specified text string and removes all rows from the datalayer where the string is not found in the column.
This element is similar to The Condition Filter element, however, it element may provide better performance because it's implemented as a native part of the Logi Data Engine and so does not need to execute script like the Condition Filter.
Apply the Contain Filter
The following example illustrates how the Contain Filter is used:
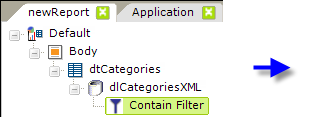
- As shown above, a Contain Filter element is added as a child to a datalayer element.
- Its Data Column attribute value is set to the column in that datalayer whose value will be searched.
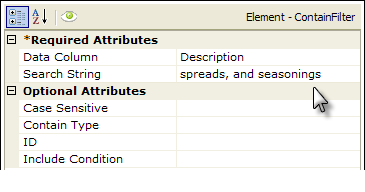
- The Search String attribute is set to the text you're searching for in the data column.
- The optional Case Sensitive attribute sets the case-sensitivity of the search. The default value is True, for a case-sensitive search. Setting it to False produces a case-insensitive search.
- The optional Contain Type attribute is set to define the nature of the search. The default value is Contains, which means the data column value must contain the search string. The other values, StartsWith and EndsWith, let you make the search more selective about where the search string occurs in the column value: at its beginning or at its end.
In the example above, the sequence of events is that the datalayer reads in all the data from the XML data file, then the Contain Filter removes all rows that don't match the criteria (Description column value contains "spreads, and seasonings"). All that remains in the datalayer for use in the report are rows whose Description column value contains "spreads, and seasonings."
Use Multiple and Dynamic Contains
1. Developers can use two or more consecutive Contain Filter elements:
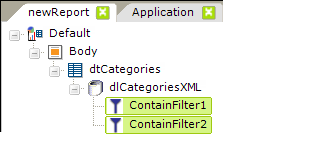
In this case, the searches will be conducted sequentially, based on their arrangement from top to bottom in the element tree. So, after the first Contain Filter is applied, only records that meet its criteria will remain in the datalayer to be evaluated by the second Contain Filter.
2. Developers can make Contain Filter elements dynamic by using tokens:

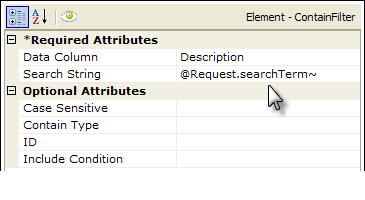
As shown above, the Search String attribute value can contain tokens such as @Request, so that comparison values are dynamic at runtime.
Sometimes it is necessary to ensure that tokens have default values when running a report. When using @Request tokens, the Default Request Params element can be used to create default values for each @Request token.
3. The Contain Filter element also has an Include Condition attribute:

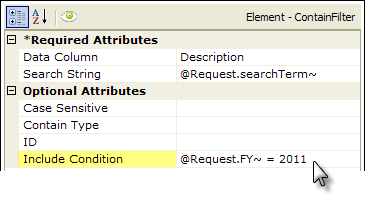
If the value of this attribute is left blank or contains a formula that evaluates to True, the element is applied to the datalayer. If the value evaluates to False, the element is ignored and does not affect the datalayer. This powerful feature allows developers to dynamically determine if the datalayer will be filtered or not.