DataLayer.Mongo Find
MongoDB is a cross-platform, document-oriented database system, classified as a "NoSQL" database. Rather than using a traditional table-based, relational DB structure, it uses a collection of JSON-like documents with variable schemas. The DataLayer.Mongo Find element retrieves data from this system, using the MongoDB Find API. This topic discusses this datalayer.
- Attributes
- Working with DataLayer.Mongo Find
![]() General information about MongoDB can be found at the official website.
General information about MongoDB can be found at the official website.
Attributes
The DataLayer.Mongo Find element has the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection ID | (Required) Specifies the ID of a Connection.MongoDB element in the application's _Settings definition. This element is discussed in more detail in the next section. |
| Mongo Collection | (Required) Specifies the name of the document collection to open. |
| ID | An optional element ID. Recommended for easier identification when debugging. |
| Maximum Rows | Specifies a the maximum number of data rows to retrieve. If left blank, then all records that satisfy the request will be retrieved. |
| Mongo Fields Document |
Specifies a Mongo "fields" document to identify the values
returned from a query. For example: { name : 1, phone_office : 1 } To vary the document content based on user or other input, use tokens, such as @Request, inside the document. |
| Mongo Query Document |
Specifies a Mongo "find" document to identify one or more
documents. Examples: Find all documents with "type" equal to "snacks". { type: "snacks" } Find all documents with "type" equal to "food" or "snacks" { type: { $in: [ 'food', 'snacks' ] } } To vary the document content based on user or other input, use tokens, such as @Request, inside the document. |
| Mongo Sort Document |
Specifies the sort order for the results of a DataLayer.Mongo Find
query. For example: { country_name : 1, city_population : -1 } To vary the document content based on user or other input, use tokens, such as @Request, inside the document. |
Working with DataLayer.Mongo Find
DataLayer.Mongo Find retrieves data from the MongoDB system. Its attributes can be used to form a "query" so that specific data is returned. It also supports a cursor, which allows results sets to be greater than 16MB in size.
In many respects, DataLayer.Mongo Find functions exactly as other datalayer elements do and, once retrieved, its data can be filtered and conditioned using appropriate child elements. Like other datalayers, it works with a specific Connection element, Connection.MongoDB, to connect to the datasource.
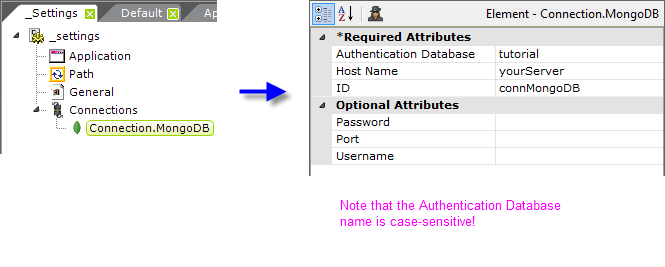
As shown above, the Connection.MongoDB element is added to the _Settings definition, beneath the Connections element. Attributes are set appropriately for the MongoDB datasource. A Mongo Params element is available for use beneath Connection.MongoDB to supply additional options when connecting to the MongoDB database. Examples of additional parameters include "connectTimeoutMS" and "maxPoolSize". Refer to the MongoDB connection options documentation for a the complete list of options.
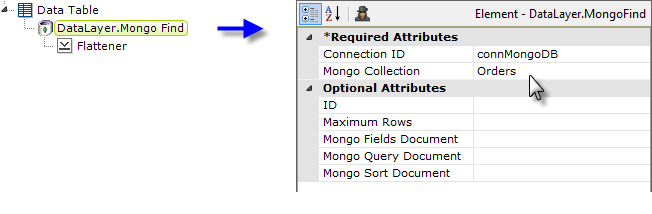
Next, in the report definition, a DataLayer.Mongo Find element is added as a child element of a data table or another data container element. Its attributes are set so that it accesses the desired MongoDB connection and data collection.
MongoDB results are often hierarchical and may consist of multiple levels of parent-child relationships. In order to work with Logi elements, the data often must be "tabularized" and this can be done by using The Flattener element.
The datalayer reads and caches the data from the datasource. You can add standard child elements beneath the datalayer to affect its contents, including:
- Filtering: Sort, group, or restrict the data
- Extending: Add virtual columns to the datalayer that contain aggregated, calculated, or totaled data values
- Securing: Limit access to the data using Logi security
- Linking: Make the results reusable elsewhere in your report definitions
Data retrieved into the datalayer is cached in XML format, in memory and/or on the web server's file system. The latter is discussed in The Logi Server Engine and may be of interest to developers working with extremely large datasets or large numbers of concurrent users.
The data read with the datalayer is available using @Datatokens, in the format @Data.ColumnName~. The spelling of the column name is case-sensitive. The data is only available within the scope of the parent element of the datalayer, not throughout the entire report definition. The DataLayer.Linked element can be used to make the data reusable in another datalayer outside this scope.
The data retrieved into the datalayer can be viewed by turning on the Debugging Link in your _Settings definition (General element) and using the resulting link at the bottom of your report page to view the Debugger Trace page. A link on the Debug page will display the retrieved data.